
From young to old, as the human body ages, it goes through a lot of stress. A sign of excellent physical health in the elderly are healthy knees.
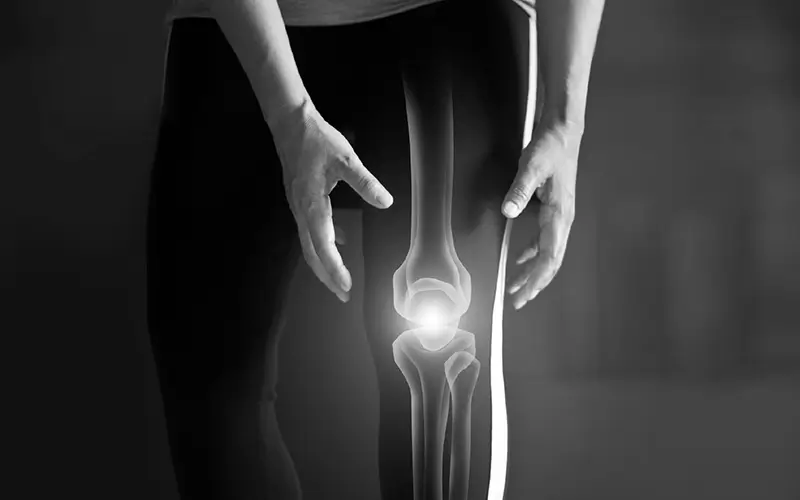
As time passes, and our body starts to age, bones and joints are the first to start deteriorating. In this day and age, everyone is leading an “on the go” lifestyle, which is coupled with intense physical movements, which results in our joints bearing all the brunt. Out of the many complex joints in our body, do you know which joint faces the most strain? You guessed it right! It’s the knee joint.
Everyday activities, such as lifting and kneeling, and any form of high-impact activities, such as jogging, and aerobics make the knee a vulnerable joint that bears a great deal of stress.
The knees are two long leg bones, held together by muscles, ligaments, and tendons. There are two groups of muscles involved in the knee, including the quadriceps muscles (located on the front of the thighs), which straighten the legs, and the hamstring muscles (located on the back of the thighs), which bend the leg at the knee. Tendons are tough cords of tissue that connect muscles to bones and Ligaments are elastic bands of tissue that connect bone to bone and provide stability and protection of the joints.1
Our knees receive four times the amount of stress for every kilo we weigh. And as we age, they face the most deterioration, making the knee joint more prone to swelling and pain. That’s why doing even the most basic activities like climbing stairs or going for a walk starts to sting.
When it comes to underlying reasons for knee pain, there could be one or many factors involved like:4
Damage during any of these can cause pain, as the tissue from joints and ligaments needs more time to heal.
Osteoarthritis is a common joint disease, also called “wear and tear” arthritis. The cartilage that cushions joints, breaks down and the exposed bones rub against each other, causing pain. Bones may change shape as Osteoarthritis worsens. It can be painful and difficult to move the joint, resulting in pain, stiffness, and interference with joint movement.2
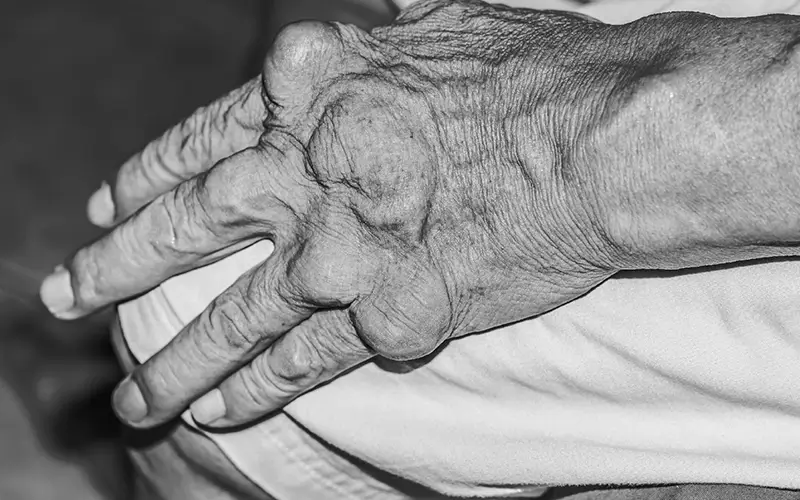
A deficiency in nutrients required for better bone health that further leads to low bone density, causing bones and joints to be brittle, leading to knee joint swelling up.
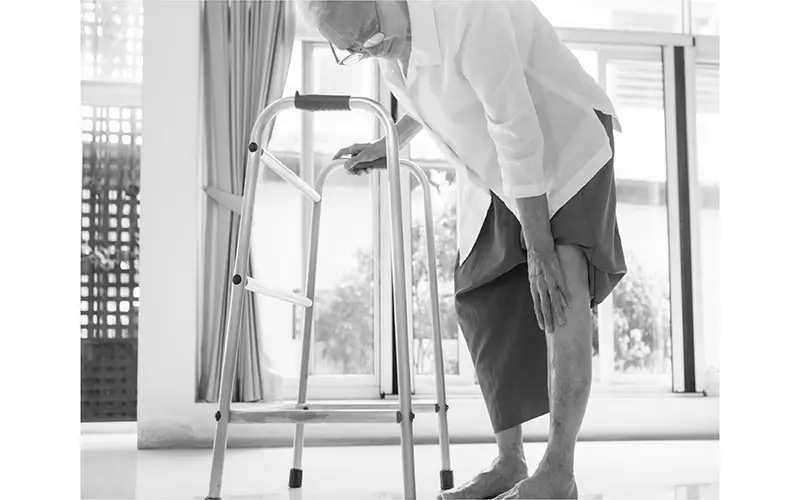

A sprained or strained knee ligament or muscle is usually caused by an external trauma like a blow to the knee or a sudden twist of the knee. Symptoms often include pain, swelling, and difficulty walking.
To treat a swollen knee, use “RICE” which stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Give your swollen knee joint some rest, apply ice to reduce swelling, wear a compressive bandage, and keep your knee elevated.1
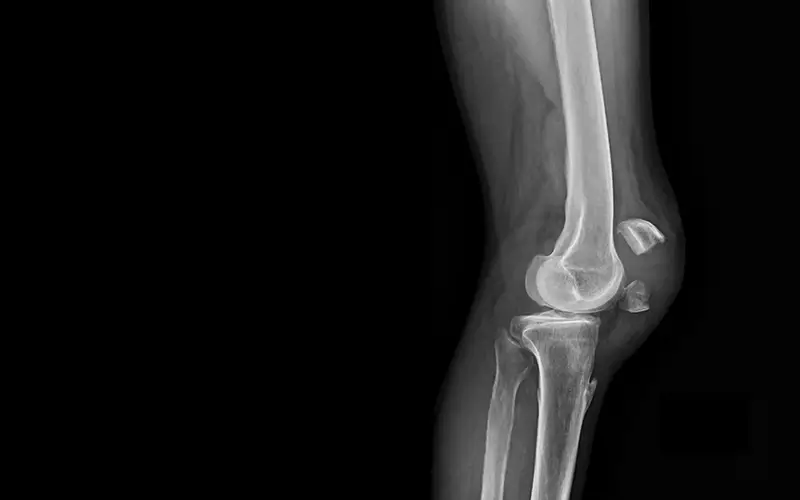
A tear or break around or behind the knee which causes swelling due to trauma or excessive external stress to the ligament.
With time, the wear and tear on the knee joints can affect the way the knee feels, functions or moves. So, if an elderly person experiences a clicking or popping sensation in the joint when they walk, bend or lunge, without pain or swelling, it indicates a mild symptom that can eventually cause knee pain and needs urgent care. But if the knee pains or swells up, along with a clicking or popping sensation, it’s best to schedule a visit to the doctor or physiotherapist for consultation.
To recover and avoid aggravating knee pain there are many other solutions that can be followed:
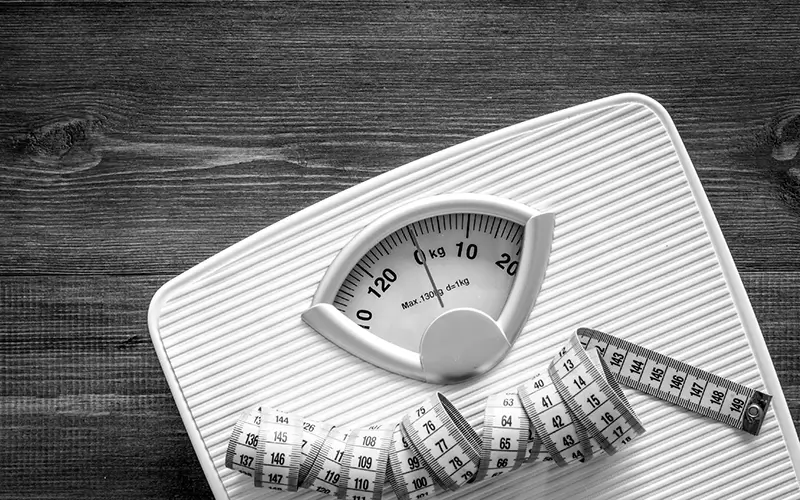

The more you weigh, the more stress you put on your joints. For people who are overweight or obese, losing weight reduces pressure on the joints, specifically weight-bearing joints like the hips and knees. Reaching or maintaining a healthy weight can relieve pain, improve function, and slow the progression of OA and help avoid knee pain.5
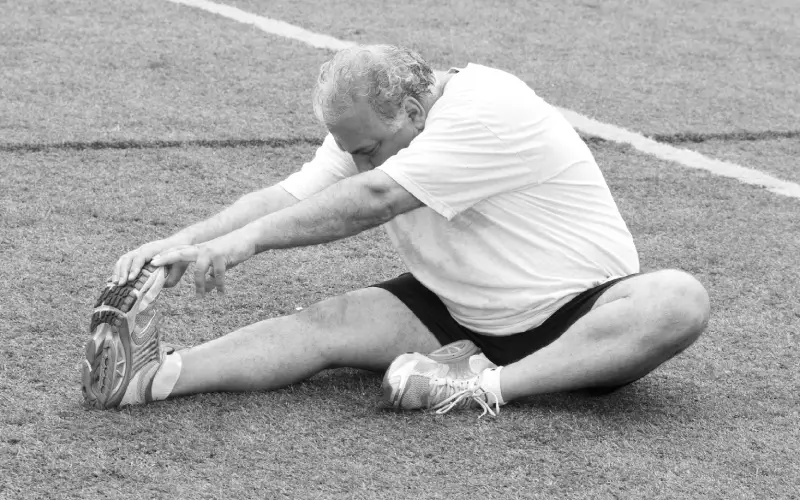

Before any demanding physical activity, mild stretching exercises like a quad, calf and hamstring stretch can help improve joint flexibility and minimize joint injuries.
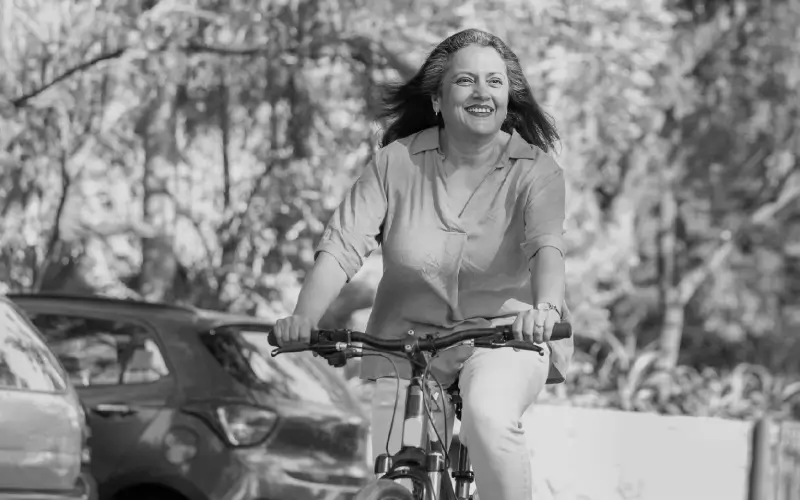

Go on long walks, use the stairs instead of the elevator, or ride a bicycle.
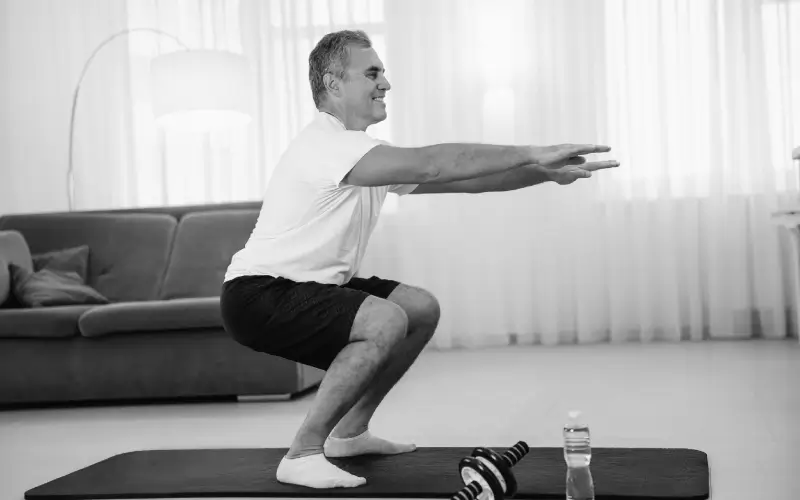

Strengthen muscles that support your knees with dynamic exercises like squats and jumping jacks.
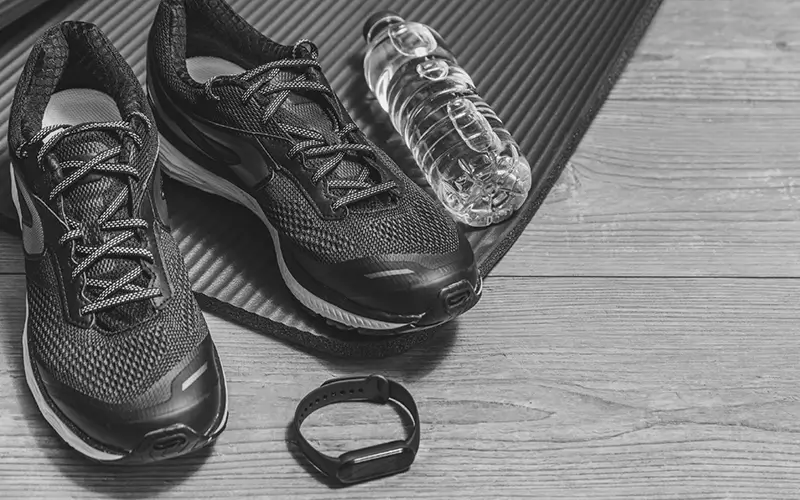

Wearing shoes that are worn out or that fail to offer adequate support can increase pressure on the knees, affecting your posture and overall form.
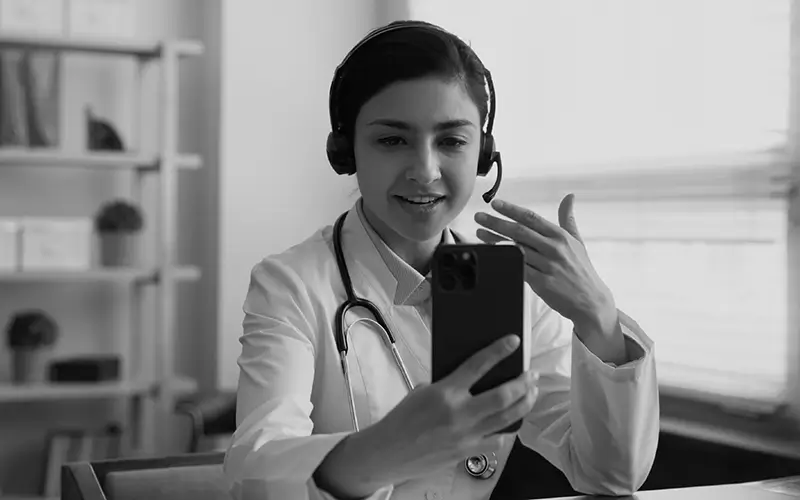

Patients can play an active role in controlling arthritis by attending regular appointments with their health care provider and following a recommended treatment plan. This is especially important if they also have other chronic conditions, like diabetes or heart disease.5
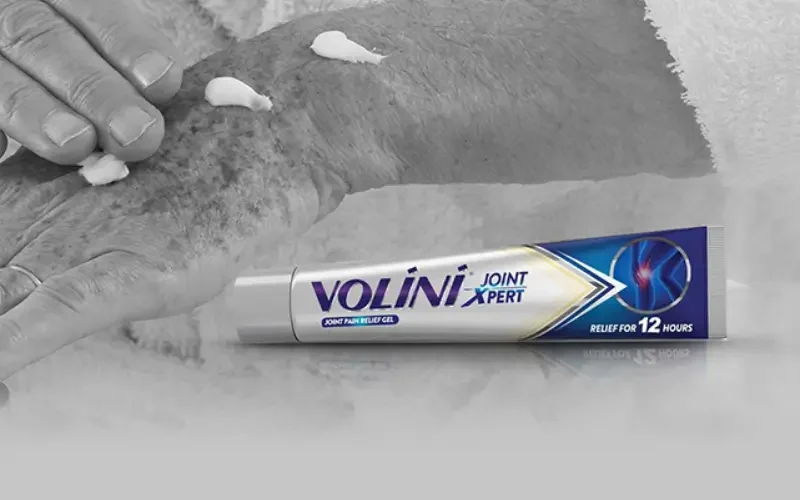

There are plenty of pain-relieving medicines that you can buy over-the-counter from a pharmacy to help ease the pain. Topical NSAIDs are the first-line recommendation for hand and knee osteoarthritis according to guidance from the only Institute of Health & Clinical Excellence (NICE).6
Volini Joint Xpert falls in that very category of topical NSAID and is formulated using the Emulgel technology with 2% Diclofenac which provides long-lasting pain relief for 12 hours. Its unique Nanogel formula helps in ensuring a faster and deeper penetration into the skin so that you can get back to doing the things you enjoy.5
So, for an additional knee pain treatment at home, that lasts long, trust the Xpert!
